- Automation & Control Gear
- Cables & Wires
- Enclosures & Server Racks
- Fuses & Circuit Breakers
- HVAC, Fans & Thermal Management
- Lighting
- Relays & Signal Conditioning
- Switches
- Batteries & Chargers
- Connectors
- Displays & Optoelectronics
- ESD Control, Cleanroom & PCB Prototyping
- Passive Components
- Power Supplies & Transformers
- Raspberry Pi, Arduino, ROCK, STEM Education & Development Tools
- Semiconductors
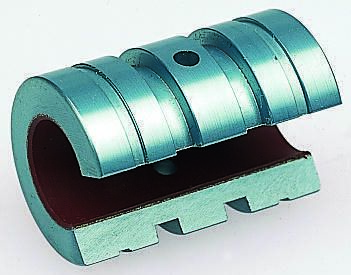
Pacific Linear Bearings
Linear bearings are designed to provide a free motion in one direction and are the most common type of linear slide, offering a smooth precision motion along a single axis linear design. Most commonly used within the furniture industry as a ball-bearing drawer slide.
Linear plain bearings are bearing elements for translation type motion (motion along a path). Unlike roller bearings, linear plain bearings move on a shaft or static guideway, as opposed to on movable component slides. Depending on the type of guiding system, the sliding layer is applied to the rigid or movable component.
RS have a great range of linear bearings ideal for most mechanical power transmission applications.
How do Linear Motion Bearings Work?
Linear Ball Bearings are housed in a linear base, with self-lubrication properties that increase reliability. Most commonly constructed from materials such as aluminium, steel and the ball bearing slides consist of two linear rows of ball bearings contained by four rods and on differing sides of the base. This low friction linear movement can be powered by either a drive mechanism or by hand.Linear plain bearings are available in a wide range of sizes and material types, suited to different applications. They come in three main configurations: closed, open and split.
Applications for Linear Bearings
Ball-bearing slide applications include delicate instrumentation, robotic assembly, cabinetry, appliances and clean room environments, which primarily serve the manufacturing industry but also the furniture, electronics and construction industries.
Linear plain bearings are resistant to shock and contamination. They offer high static load capacity and low wear and make little noise. These characteristics make them suitable for applications where the bearing position must be low maintenance or maintenance-free, or where lubrication is either impermissible or undesirable. They are found in everyday applications including:
- Printers
- Lab equipment
- Thermoperformance
- Additive manufacturing
- Welding machines
- Stone saws and heavy-duty cutters
- Assembly and inspection stations
- Seat adjustment and shock absorption